- Home /
- Green solutions /
- What is the Greenhouse Effect? Causes, consequences, and how to control it
What is the Greenhouse Effect? Causes, consequences, and how to control it
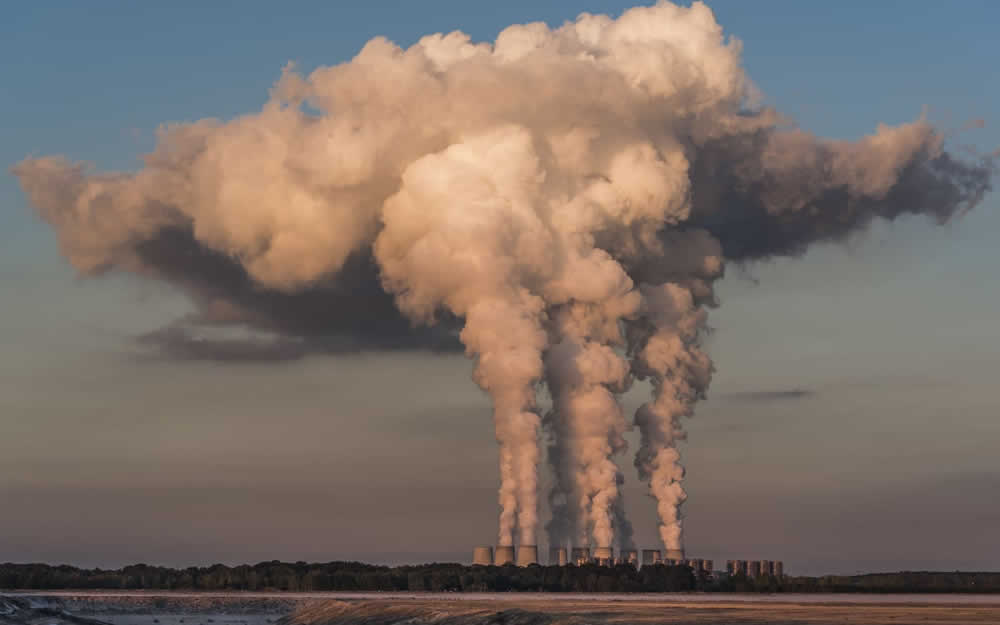

Greenhouse effect, climate change, global warming: we often associate these terms improperly, thinking that they are directly related. Not everyone knows that the greenhouse effect is actually a perfectly natural phenomenon, a spontaneous system that preserves the Earth's thermal balance, allowing life to emerge and evolve.
What exactly happens in the atmosphere when we talk about the 'greenhouse effect'? What causes it? How can we contain the risks that arise from it?
Greenhouse effect: a definition
The greenhouse effect was first described in 1896 by a Swedish scientist, Svante Arrhenius; since then, it has become one of the most debated and discussed topics in the global scientific community for its consequences on the climate and the environment.
But how does the greenhouse effect work? To reach the earth and warm the surface, solar rays pass through the atmosphere and are then reflected as infrared. Before reaching the earth, however, the heat is filtered by some gases present in the atmospheric layers: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
These substances create an effect similar to that of a greenhouse, containing the dispersal of heat and maintaining a stable earth temperature, thus making the planet compatible with life.
Greenhouse effect and global warming
The greenhouse effect is therefore a natural phenomenon that favours life on the planet. But why do we associate it with an increase in temperature? If the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere increases, the filter becomes even more powerful and retains more heat.
The risk of the greenhouse effect lies entirely in the abuse of anthropogenic gases, that is, those produced by human activity. If greenhouse gases increase, the Earth's thermal balance is altered, contributing to global overheating.
Anthropogenic causes of the greenhouse effect
The main cause of the increase in the effect is the uncontrolled release of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These substances reach the atmosphere through human activity, from the use of spray cans to intensive agriculture, to urban development.
The abuse of fossil fuels has indeed led to a huge amount of CO2 emissions, one of the most important greenhouse gases. Another determining factor for the greenhouse effect is deforestation, as the disappearance of forests and plants reduces the ability of trees to absorb CO2.
Consequences of the greenhouse effect
We can observe the negative consequences of the increase in the greenhouse effect in every aspect of terrestrial life: from society to nature, to the economy and the risks to health.
- Rising temperatures, resulting in melting glaciers and rising sea levels;
- Extreme weather phenomena, such as droughts, water bombs and desertification;
- Loss of biodiversity, already in crisis due to deforestation;
- Spread of diseases and bacteria;
- Loss of productive agricultural land;
- Reduction in the availability of potable water.
How to control the greenhouse effect?
The only way to contain the greenhouse effect is to reduce anthropogenic gas emissions: changing production patterns, changing habits and lifestyles in order to avoid the use of fossil fuels as much as possible. Here are some individual and collective solutions to curb the greenhouse effect, reduce one's carbon footprint and preserve the Earth's thermal balance:
- Use renewable energy sources: promote the use of clean and renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind and hydropower;
- Energy efficiency: reduce energy consumption through the use of more sustainable technologies, such as thermal insulation and renewable energy sources;
- Sustainable mobility: encourage the use of public transportation, bicycles and electric cars, to avoid individual fossil fuel leakage;
- Sustainable agriculture: promote sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming;
- Forestry: promoting sustainable forest management can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, as plants absorb CO2 during chlorophyll photosynthesis;
- Public policies: public policies can play an important role in reducing GHG emissions by implementing sustainable practices, regulating polluting activities, and investing in clean and renewable technologies;
- Awareness and education: sensitising children to respect the ecosystem and educating adults on environmental responsibility is key to adopting sustainable behaviours.
Each of us can contribute to reducing global warming and curbing the greenhouse effect in our daily lives. For example, choosing to use refill containers for consumption of water especially during naturalistic excursions
On the Acea Waidy Wow app you can find all the city's water points through a handy interactive map, to start your own little sustainable revolution right from your smartphone!